One of the most important decisions you’ll make for your business is whether to partner with Google in promoting your website, brand, products, or services on its ad network. With Google, your business will have access to over 100 million sites on the web that will help you display your ads, thus widening your audience reach.
Once you choose Google as your advertising partner, the next thing to do is find out where to advertise. Just as you should know whom you’re creating your ads for or what objectives you’re trying to achieve, you should likewise identify which sites can potentially boost your advertising game.
After picking a site on the Google Display Network (GDN), you’ll also need to determine which section of the site you want your ads to be. The space above the fold is considered the most lucrative ad space since it’s the first thing people see upon reaching a particular web page. However, other advertising spots within a website are equally effective in catching the attention of online visitors.
In this post, you’ll learn how to use Google ad placements effectively and access the Google ads placement list as we discuss relevant ad placement strategies and present a round-up of ad types and formats, corresponding specs, and other key details.
3 GDN Ad Targeting Strategies
Google prides itself on its placement targeting techniques designed to position your ads more strategically. Here are the three main strategies for ad placement and when to use each.
1. Managed placement
This targeting method allows you to choose which websites, apps, app categories, videos, or channels within the Google Display Network placement list you want your ads to appear in. Your choice can be based on where your target audience spends more time, garnering you more control over the visibility of your ads and ensuring your ads are seen by the target audience.
2. Keyword targeting
Google’s system matches your ads with GDN sites whose central theme is related to the set of keywords you’ve chosen to target, especially if you don’t have any specific websites in mind and want Google’s algorithm to find websites with the highest potential.
3. Topic targeting
Topic targeting shows your ads on any pages on GDN or YouTube with content related to your selected topics. It uses Google’s algorithm to match your topics with the website’s content and is helpful if you’re not 100% sure about your selected keywords.
Although you’ll be faced with a range of other ad targeting options, these three will be your primary strategies, so it’s good to know how they work to ensure that you’re hitting your targets with your Google display ads placements.
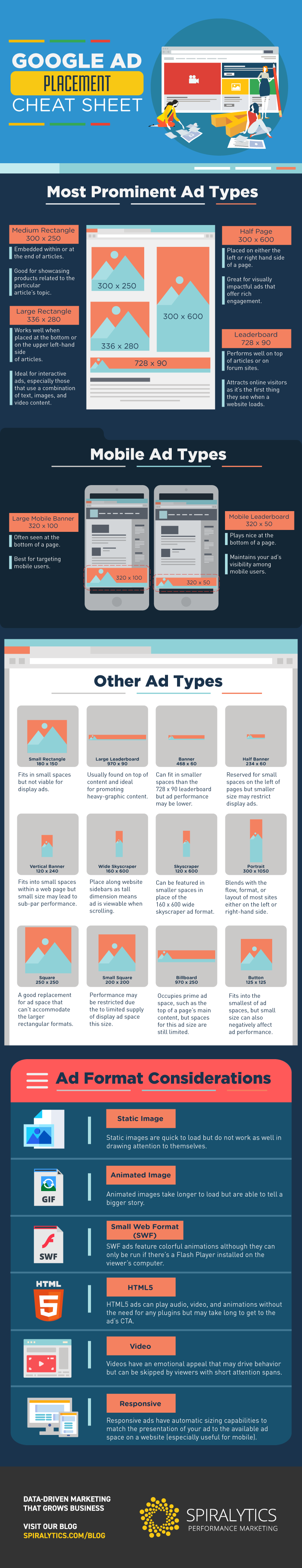
Google Display Network Ad Types
Aside from strategically choosing and establishing your Google display placements, you must also consider ad types.
There are at least 18 possible ad types on the GDN (potentially more depending on what country you’re in) – the largest ad network on the web. Each comes in a different size and shape, each playing an important role in determining where they’re typically featured on a website. You’ll want a location where your ads can have maximum exposure and blend well with the site’s features.
- Billboard (970×250)
- Large leaderboard (970×90)
- Leaderboard (728×90)
- Banner (468×60)
- Large rectangle (336×280)
- Large mobile banner (320×100)
- Portrait (300×1050)
- Half page (300×600)
- Mobile leaderboard (320×50)
- Medium rectangle (300×250)
- Square (250×250)
- Half-banner (234×60)
- Small square (200×200)
- Small rectangle (180×150)
- Wide skyscraper (160×600)
- Button (125×125)
- Skyscraper (120×600)
- Vertical banner (120×240)
For instance, wide but short ads, such as leaderboards and banners, can usually be found on the top section of a page. Wide-sized ads are very popular due to their reader-friendly format, which enables readers to absorb information in a word-by-word sequence. By contrast, tall but narrow ads, such as wide skyscrapers, are ideally placed along the sides, so they don’t restrict the flow of the page’s content.
Moreover, the type, dimension, and other technical specifications will dictate what you can feature in your ads. You can’t use images if you’re choosing small ad sizes, which can only accommodate text ads. So, if you want to promote your brand, product, or service using multimedia objects, your advertising has to lean toward banners and billboards.
3 Types of Google Display Ad Formats
Along with ad size, you should also consider the type of ad format to use. Display ads on Google generally fall into three types: static, animated, and interactive. Each type has its pros and cons in design, user experience, and efficiency.
1. Static Ads
Static images are your basic banner or square ads that surround a page’s content. They may contain your brand logo, text, CTA, and imagery but are void of motion and other interactive elements. Static ads can be a useful tool in marketing, especially when your brand already has an established following.
However, one downside to using static banners is the so-called “banner blindness,” a phenomenon where users tend to ignore ads or information presented in a banner-like manner. Online advertising statistics back this up, as apparently, online users opened only half of the 1,700 banner ads served to them each month. That said, you should work at producing static ads that initiate a point of contact or drive conversion or sales from customers through concise copy and design.
2. Animated Ads
However, unlike static ads that display the call-to-action prominently at all times, an animated ad may be slower to get the CTA out to the viewers. Hence, there should be a balance between eye-catching animations and the conciseness of your message to keep the viewer’s eyes on your ad.
3. Interactive Ads
Interactive ads are likewise used to tell narratives and create a personal appeal with your audience in a more creative fashion. Interactive ads require action from users or viewers, such as answering a simple question or trivia to try out a product or service for free.
You can design your ads in multiple formats depending on the ad size you choose. For example, you can serve static banner-size ads in JPEG, PNG, or one-slide GIFs; animated banners using a series of GIF frames; or interactive banners in SWF. Whether you’re using static or animated images, your file size should not exceed 150KB.
Video ads can lead to strong audience engagement, with more and more people being drawn to video for giving life to your content. People who’ve watched your videos can also be a great audience for retargeting ads. Keep them under 3 minutes to encourage viewers to watch until the end. Putting subtitles can also improve viewership since there are people who turn off the sounds from their computer and use that as their default setting.
5 Most Effective Google Display Ad Placements
Here are the top performing ad placements according to Google.
1. Medium Rectangle
Every time your ad is shown on any site within the Google Display Network, it counts as an impression. The medium rectangle has the highest ad impression share of 33%, which represents a third of all ad impressions on the GDN.
This makes the medium rectangle the most popular display ad type mainly because its 300 x 250 size makes your ads visible enough, which is helpful in boosting traffic to your website. Its size is also ideal for placement in conspicuous places that people see when a site loads, including the top or end sections of the screen, as well as within an article itself.
2. Large Rectangle
Ads in a 336 x 280 large rectangle type may be the second most effective ad size, especially when placed beside an article toward the upper left-hand side. This ad size complements how people view a website’s contents, which is from the top left corner toward the end in a left to right direction.
3. Leaderboard
At 728 x 90 pixels, you’ll usually see leaderboard ads in the header portion, which is a section above the fold or on the upper half of the screen. A standard leaderboard can contain both text and images, and captures a 32% ad impression share on the GDN.
4. Half Page
The half page is another popular ad type, which belongs to the larger ad units with a 300 x 600 dimension. Half-page ads are big enough to accommodate a mix of copy, image, offer, and CTA button. The click-through rate (CTR) and click-to-conversion-rate (CTCR) of half-page ads are impressive at 253% and 37% respectively. That’s significantly more than medium rectangle ads.
5. Large Mobile Banner
Large Mobile Banner is designed to target smartphone users. It’s usually placed on the bottom of a page and has a dimension of 320 x 100 pixels, which make for good viewing across mobile devices.
Google AdSense Heat Map
You can also identify the best location for your ads through the Google AdSense Heat Map, a strategy which is based on the idea that certain sections in a website are more effective than others. This approach involves identifying the way that web users interact with a particular site, so you can more or less predict where readers are more likely to look and therefore see your ads.
For one, ads that fit above the fold are considered gold due to the fact that everyone can immediately view this section once the page loads on the browser. It’s also recommended that you place your ads as close as possible to the primary content, so that your ads occupy the center of the screen.
By being aware of what factors can possibly affect ad placement, you can make informed decisions on how to better position your ads. Still, you should remember that each website is different, so testing your ad placements regularly can optimize performance and lead to more positive results.
Key Takeaways
While Google Ads is specific enough to tell you what ad types and formats to use, it’s still up to you how you’re going to get the most out of your ad placements. A few best practices include finding out which sites your audience frequents, determining the kind of response or behavior they show toward ads, and then creating ads for all possible sizes for every website to help you find the most effective options.
Ultimately, these insights can dictate your campaigns’ best Google ad placement. And don’t forget to set up your ads with a focus on helping customers with their needs through your offers or recommended solutions.
To boost your local campaigns, consider using pay-per-click in the Philippines, which allows you to target specific audiences and optimize your ad spend for maximum results.
Struggling to generate returns from your Google Ads campaigns? We help our clients grow and optimize their PPC funnels to drive the best leads at the lowest acquisition costs! Find out more.







